Emerging Trends in Business Valuation for 2025 AI Tech and Market Insights
Emerging Trends in Business Valuation for 2025: AI, Tech, and Market Insights
Introduction to Emerging Trends in Business Valuation for 2025 AI Tech and Market Insights
Business valuation is in one of the most transformative decades in decades. With the growth of digital ecosystems, the rise of artificial intelligence is becoming the new normal, and the world is becoming globalized, faster than ever before, the companies are finding themselves needing new tools and analytical frameworks to perceive value. Valuation professionals, investors, and corporate managers, especially those involved in business valuation Singapore practices, are becoming more aware that traditional models (like discounted cash flow analysis or similar company multiples) are not adequate anymore in new conditions of fast a technology disruption and new intangible-based new business models. The article in question pays particular attention to the ways in which AI-enabled analytics is transforming the contemporary valuation practices, as well as why this innovation should be important to contemporary deal-making, capital raise, and strategy formulation. Through the review of real-life examples, industry case studies, and emergent approaches, organisations will be in a better position to be ready to face a valuation environment in which technology is no longer a competitive luxury but an integral component of the competitive advantage.
1. The Rise of AI-Driven Valuation Models
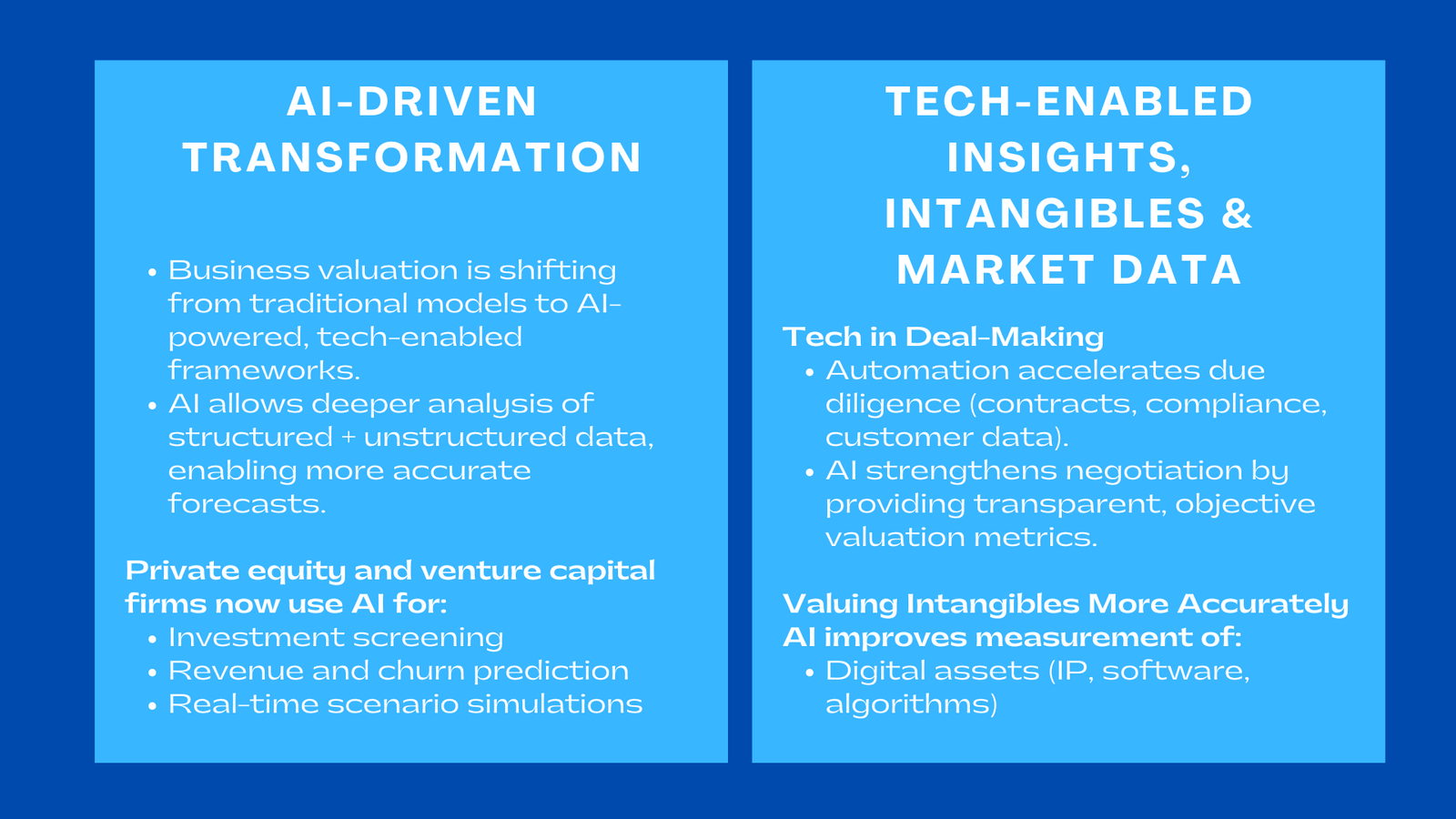
1.1 Transforming How Analysts Use Data
A significant development in 2025 is the widespread adoption of AI-driven valuation models, which are reshaping how analysts gather, interpret, and forecast financial information. Rather than using only past performance, or only a small amount of market inputs, AI systems are able to examine large amounts of structured and unstructured data, including macroeconomic indicators and examples of customer behaviour. Indicatively, AI tools are being used more often by private equity companies to screen investment targets by detecting trends in revenue stability, churn risk, or cost efficiency which would otherwise require analysts weeks to consider the same manually. Thousands of simulations can be performed using these models in order to find more realistic ranges of valuations given the uncertainties of the real world.
1.2 More Precise Projections of the technology driven sectors.
The machine learning-based predictive analytics can also be used to the advantage of companies dealing with high-growth industries like fintech, e-commerce, or SaaS. Impactful forecasting approaches also tend to be limited in their capability to model unstable pricing approaches, frequent revenue streams, or user metrics with quicker rates of transformation. Accuracy has been enhanced by AI which incorporates behavioural analytics coupled with real-time market trends. As an example, SaaS investors find it easy to forecast the future cash flows of a company based on historical customer usage, frequency of usage and volume of support tickets with the aid of AI-enhancing their valuation assumptions and minimizing the application of general industry metrics.
2. Leveraging Tech-Enabled Insights for Better Deal-Making
2.1 Enhancing Due Diligence Processes
Deal teams across venture capital, private equity, and M&A advisory increasingly rely on tech-enabled valuation insights to accelerate due diligence and reduce deal risk.Financial statements, operational data and market intelligence can be handled by automation tools in a few minutes as opposed to days by the analysts. This gives it a competitive advantage in high paced markets where consumers are forced to act on the market within a short period. To illustrate, there are M&A companies today that apply natural language processing to scan through large collections of documents, typically contracts, customer messages and compliance filings to identify valuation-related risks including revenue concentration, supplier concentration, or upcoming litigation.
2.2 Enhancing the Results of the Negotiation.
The use of technology in valuation also enhances the dynamics of negotiation. The AI-based models can assist buyers and sellers in developing more solid data to support their pricing positions when it comes to valuation negotiations. An example of this is a startup that has raised a Series C round and is basing their valuation on a cohort analysis generated by AI and the investors presenting a valuation that is based on churn risk generated by AI. Due to the increased reliance on more objective metrics by both parties, the process of negotiations tends to be more transparent and data-oriented, which results in the fairness and effectiveness of deal outcomes.
3. New Methods of valuing intangible asset.
3.1 The code of conduct outlines the requirements of valuing digital assets more precisely.
The evaluation of intangible assets is among the most complicated fields of contemporary valuation, particularly digital one. Increasing value of intellectual property, software platform, and algorithm-driven business models is also being made possible by AI and data analytics. Any company that has a high level of technological differentiation, a proprietary AI engine, or cybersecurity system, or a digital marketplace, can now have a way to measure long-term value creation by these assets. As an example, AI technology has the potential to screen patents according to the number of citations, relevance to innovation, legal viability, and competitive effect, enabling companies to know which assets are generating strategic value in the process of acquisition or capital raise.
3.2 Customer Data and Behavioural Analytics.
The relationship with customers and brand strength are some of the primary intangible assets, and nowadays technology allows analyzing the lifetime value of customers, retention patterns, and acquisition efficiency in more depth. More retailers and online platforms are adopting the use of AI and behavioural analytics in their valuation processes to simulate the financial value of customer loyalty, brand sentiment, and engagement with their user community. This is especially applicable to D2C brands or companies that are subscription-based and in which customer loyalty is frequently stronger in determining value than financial metrics.
4. Valuation under the Influence of market Insights.
4.1 Valuation input of Real-Time Market Data.
The larger market environment is even more influential in the valuation estimates in 2025. As financial markets have become more vulnerable to macroeconomic factors, businesses and investors currently use real-time market data to revise the valuation assumptions. The AI machines monitor movement of interest rates, currency, commodity and industry-specific performance data then convert this into dynamic valuation models. As an example, a manufacturing company that faces the risk of volatility of raw materials can adapt its values forecasts, taking into account AI-based forecasts of the price of a commodity, providing lenders or investors with a more realistic perspective of the potential risk.
4.2 Sector-Specific AI Models
Sector-specific AI valuation tools are being implemented in high regulatory industries (such as healthcare, energy, or telecommunications). These systems include regulatory changes, restriction to market access and policy risk factors in valuation models. An example of a renewable energy company can utilize AI to model valuation conditions depending on potential changes in policies on carbon pricing or renewable subsidies, and so, would allow investors to consider the viability of these projects in the long-term and risk-adjusted returns.
5. Implications in Practice
5.1 Capital Raising and Investor communications.
Firms that gain capital have an opportunity to capitalize on AI-enhanced valuation information to build investor trust. Organisational financial models can also look investor-ready and more credible when preparing pitch decks, valuation reports and even with having an advanced analytics regardless of the situation they are in. This is because it is essential in competitive funding situations where investors prefer businesses that have good data capabilities. An example of a logistics startup can employ AI-based demand forecasting to show the next inflection point of growth which allows reaching a higher valuation during fundraising.
5.2 M&A Integration and Post-Deal Value Tracking.
The process of valuation does not stop at the time of closing the transaction. The AI tools assist the companies in monitoring whether the business they have acquired is performing as per the valuation assumptions. Continuous analytics can assist post-merger integration teams to observe revenue synergies, cost reduction developments, customer retention, and cultural adjustment. This feedback mechanism enables the acquirers to optimize strategies at an early stage so that anticipated value creation may be translated into calculable financial performance.
Conclusion
The future of business valuation in 2025 is changing fast due to the impact of artificial intelligence, data analytics, and real-time market intelligence. The incorporation of AI-driven models is changing the way businesses analyze financial results, appraise immeasurable resources, perform due diligence, and close deals. Those organisations that adopt such emerging trends will be able to access more realistic forecasts, deeper customer insights, and stronger valuation arguments. AI will gain greater insight into valuation techniques as it is advanced and will provide greater accuracy and strategic direction. Going forward, those companies that invest in AI-enabled valuation potential early will be in a better position to manage market uncertainty, improve the results of deal-making and evoke long-term competitive benefit.












