Certified Share Price Analysis Course
Share Price Analysis: Factors That Influence Market Valuation
Guide on Certified Share Price Analysis Course
The stock market is said to be a mirror of how a company performs and how the investor feels about the company, but the share prices cannot be anticipated to act in a certain manner. Every price move is behind the elaborate network of economic pointers, company fundamentals and action motives.
The knowledge of the share price analysis assists investors and analysts to identify what influences such changes and what the actual value of a stock in the market could be. It is not merely about saving or spending figures on a display screen but reading between the lines to determine what they convey about profitability, confidence as well as future possibilities.
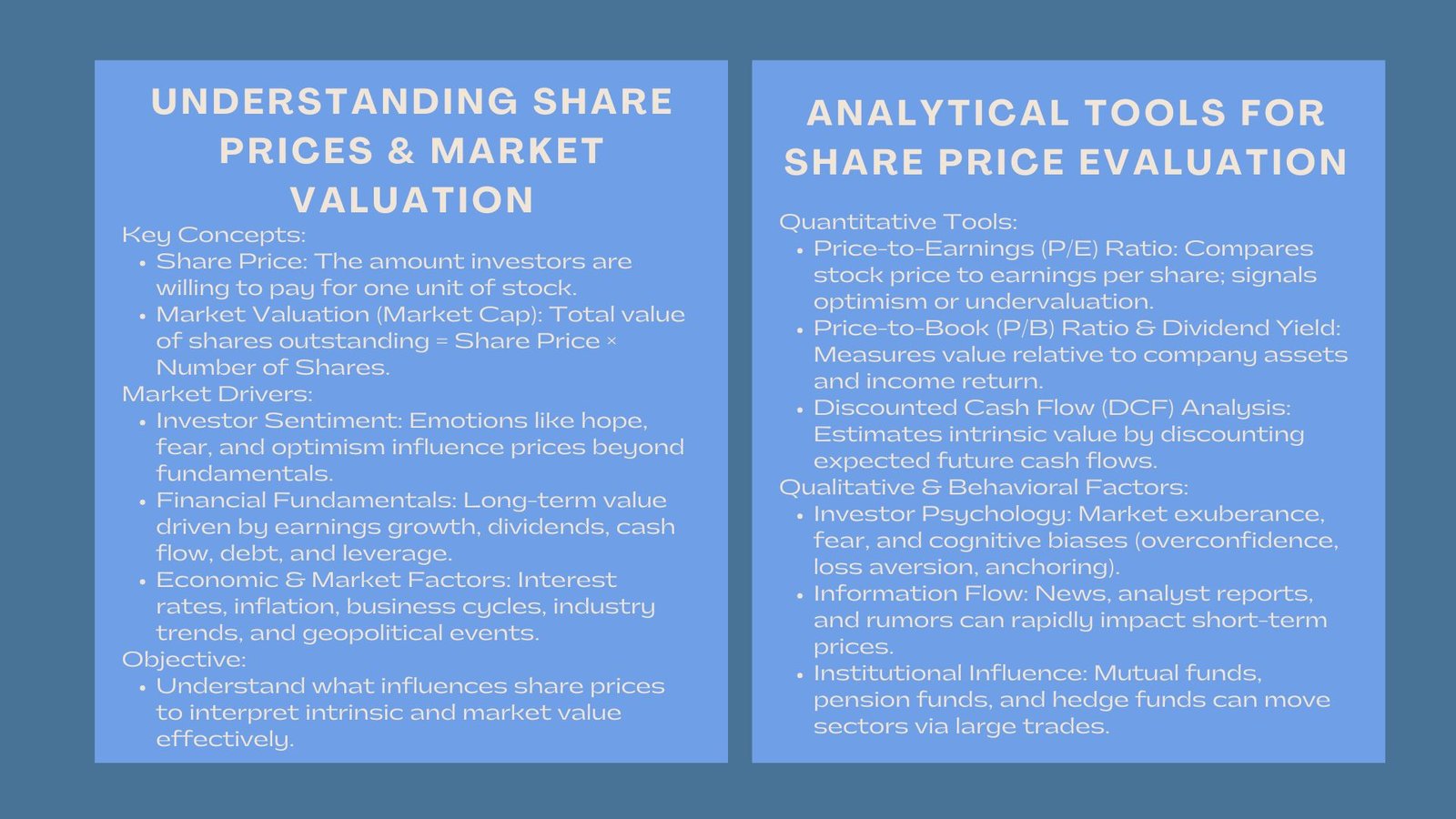
Meaning of Share Price and Market Valuation.
In essence, a share price is the amount that investors are ready to pay in order to own one share unit in a business. The market valuation or market capitalization refers to the total value of shares outstanding of the company. It is a fast method of measuring company size and level of perception by investors, even though it does not necessarily indicate intrinsic value.
How Market Valuation Works
Market value is obtained as price of the share multiplied by the outstanding shares of the company. As an example, a company which has one hundred million shares with a price per share of 10 dollars will be having a market capitalization of 1 billion dollars. Nevertheless, this figure may change drastically based on the demand of investors and the external factors.
The Investor Sentiment Role.
Surprisingly, emotions and psychology are significant players in the market pricing. Both hope or expectation of growth or the fear of economic declines can cause prices to be well above or below the fundamental value. This is why analyzers should strike a balance between technical information and sentiment analysis of stocks.
Basic Elements that Influence Share Prices.
Although short-term volatility usually gets the headlines, the real long-term movers of the share prices are financial fundamentals of a company and position in the industry.
Earnings and Revenue Growth
One of the best determinants of the value of the company is its profitability. Investors would reward stable increase of earnings because this will be an indication of stability and capacity to reinvest the profits. A stock market boom is witnessed when firms declare above-average quarterly earnings.
Dividends and Cash Flow
High cash flows enable firms to make dividends – an indicator of financial well being and shareholder value. Income-oriented investors tend to invest in dividend-paying companies as being less risky.
Debt and Leverage
Excess leverage may destroy confidence. Debt-to-equity ratios help investors to know whether a company has the ability to fund its debt. Healthy balance sheets are likely to get higher values in the long-term.
Market and Economic Influences.
Interest rates and inflation.
Stock valuations can be very impacted as a result of interest rate movements. The increase in the rates by the central banks will make borrowing more costly and therefore will cut consumer spending and corporate profits. On the other hand, reduced rates will increase equity markets.
Also inflation demeans the purchasing power of future income and investors can demand higher returns, which may cause a decline in share prices.
Cycles in Economic Growth and Industry.
The pricing of shares is strongly connected with the overall economic trends. During booms, the earnings of the corporations are boosted by the increase in demand, whereas recessions are likely to reduce valuations. The movements of stocks are also subject to sector-specific cycles e.g. technology boom or commodity downturns.
Geopolitical Risks and Global Events.
Market corrections may occur abruptly due to geopolitical tensions, trade disputes and global crises. Multinationals are especially vulnerable to fluctuations in currency and regulation of major markets.
Share prices evaluation analytical tools.
In order to make factual investment decisions, analysts utilise both quantitative and qualitative tools.
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
It is a widely used ratio that involves the comparison of the current share price of a company to its earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio has a possibility of showing optimism as to future growth whereas a low P/E would be a sign of under-estimation or poor outlook.
Price to Book (P/B) Ratio and Dividend Yield.
The P/B ratio is used to compare the market value to the book value of the company – it is applicable in assets rich industries. Dividend yield on the other hand reveals the extent to which investors get a certain amount of return in terms of share price.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis.
The DCF analysis would determine the intrinsic value by estimating the future cash flows and discounting them to the present value. This assists in knowing whether a stock is overpriced or underpriced in the market. Many analysts rely on advanced share price valuation models for DCF and market comparison analysis to produce consistent, data-driven insights for investment decisions.
Behavior and Psychological Factors.
The Psychology of the Market and the Psychology of the Crowd.
Short-term volatility is usually caused by investor psychology. Bull markets may cause valuations to become vastly overstated by optimism – which is the so-called market exuberance. On the other hand, opportunities can be undervalued in case of fear related sell-offs.
Information and News Flow
Media reports, analyst grades and company disclosures can have a substantial effect on short term price changes. Even news rumors or hypothetical news can turn the sentiment of the investors in a short time.
Emotional Biases of Investment.
Some of the cognitive biases such as overconfidence, loss aversion and anchoring affect the interpretation of data by investors. Being aware of such patterns of psychology is a determinant of why markets may not necessarily be rational.
The Institutional Investor Factor.
The institutional investors like mutual funds, pension funds and hedge funds have a massive impact on the valuation of the market. Their buying and selling amounts and rebalancing of the portfolio can change whole sectors.
Fund managers often use professional equity valuation and share performance analysis services for institutional investment strategies to ensure that capital allocation aligns with long-term performance goals and compliance standards.
Through a methodical evaluation of the basics, risk and prospects, institutional investors help in an efficient price discovery in the financial markets.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis.
Effective share price valuation is one that blends technical and fundamental views.
Technical Analysis
The strategy is centered on trade charts and the trading trends to forecast the future trend. Analysts examine support and resistance levels, moving averages, and other momentum indicators in order to determine entry and exit points.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis on the other hand analyzes the business model, management quality and financial performance of the company. It aims at finding out intrinsic worth – the price a sensible investor is to pay depending on the long-term potential.
Combined, these strategies provide a better perspective on the actual value and status of a firm in the market.
Conclusion
The art and science of share price analysis. It involves a combination of financial measures, economic data, and psychology of people to discover what is really motivating business value. The short-term trends are usually unpredictable but the long-term trends are normally in line with the fundamentals of a company and its strategic performance.
To the investor, being able to master these factors will result in improved decision-making and better interpretation of how the market values things. In a world that has been created due to unpredictability, knowledge is the surest type of investment.












